
The next generation of wireless technology, 5G, is expected to open a future of new and exciting possibilities for enterprises. With a speed that can reach up to 10Gbps, theoretically, 5G can be 100 times faster than its predecessor, 4G LTE, and holds great potential to anchor enterprise digital transformation.
If 4G-Long Term Evolution (LTE) revolutionized the business ecosystem by enabling high-speed data services on mobile, the 5G wireless technology was designed for unlocking real-time decision-making and revolutionizing the customer experience.
Looking back, 4G has aided internet users in making on-the-go crystal clear video calls, stream high-quality data, and exchange information promptly. Still, the wireless standard could not evolve as a trusted alternative to a dedicated wireline pipe. For example, even in a remote work environment, most employees rely on fixed-line links to attend critical video conferencing calls or transfer extensive data.
However, the widespread rollouts of the next generation networks could remarkably transform how enterprises connect and deliver services. The unparalleled network speeds and enhanced bandwidth will enable business users
to do superior quality HD or 3D calls without lags. From augmented reality to artificial intelligence-based data-driven applications, 5G will accelerate a new wave of cutting-edge innovations, empowering businesses with much-needed speed, power, and capacity to exchange reliable and real-time information.
Transforming enterprise ecosystems
One of the most significant advantages that 5G offers is an extremely low latency rate, the transmission time between sending and receiving information. For mainstream adoption of autonomous cars, remote delivery of critical healthcare, and all-inclusive adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT), the industry needs exceptional quality bandwidth and low latency.
The success of mission-critical applications such as connected cars depends on reliable and unblemished connectivity that supports real-time communications and various sensors that help them operate with precision. Even a split of network instability or unexpected network lag can cause fatal road accidents. By leveraging 5G technology, applications can run at a trailblazing speed on a network with an extremely low latency rate, as low as one millisecond (1ms).
According to a survey titled, Maximizing the 5G opportunity for enterprise, conducted by EY, various industries are currently at the different trajectory of their 5G investment curves. The survey reveals that while the journey toward 5G may be in the earlier stages, 5G adoption levels are expected to grow considerably in the next couple of years. “Currently, 15% of enterprises are investing in 5G, with an additional 54% planning to invest in the next one to three years. By the end of 2022, levels of 5G investment will be on par with IoT,” the survey projects.
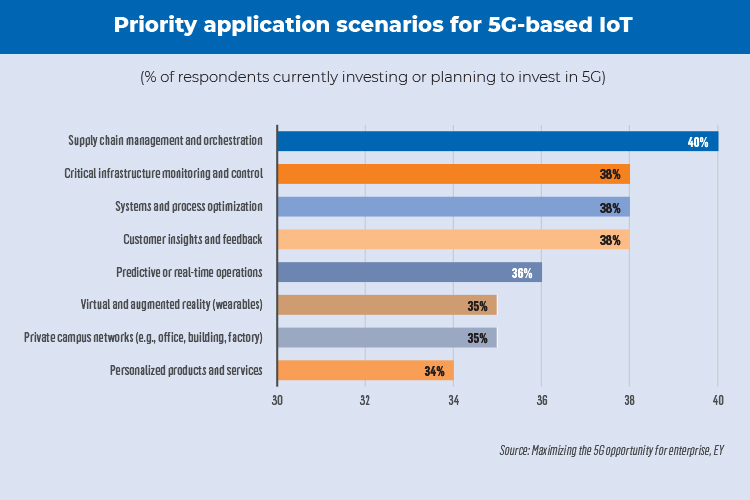
Let’s look at how 5G could enable some sectors to redefine themselves.
Transport and logistics: 5G deployments are likely to disrupt the transport sector. While it is too early to predict all the possible use cases, some emerging trends indicate the upsurge of connected and autonomous vehicles and real-time visibility and control over transportation systems. The ubiquitous 5G networks in metros and cities will enable public transport inspectors to get real-time intelligence to plan traffic movements, track emergency vehicles and anticipate transport capacity.
For example, during a medical emergency, every single minute is critical in securing a patient’s life. Hence, the inbuilt 5G-enabled intelligent traffic management systems can ensure that the emergency vehicle finds congestion-free routes to reach the hospital in time. And if the ambulance is 5G-enabled, doctors would monitor the patient’s condition remotely through sensors and provide necessary guidance for efficient pre-hospital care.
A survey from Moor Insights and Strategy reveals that for 90% of logistics and shipping providers, lack of supply chain visibility is one of the biggest challenges impacting their operational efficiency.
For logistics companies, 5G will drive significant productivities as it will enable them to monitor, track and check inventories consistently, minimizing the chances of revenue leakage.
In the future, the 5G technology can be beneficial to bring the concept of smart highways into reality to minimize deadly road accidents and congestion. The built-in smart sensors of connected vehicles would communicate and exchange data for giving timely warnings in case of any road instabilities, accidents, or traffic congestion, helping them reach the desired destination efficiently.
Countries like China, Finland, and Hong Kong have already developed prototypes in this direction and testing the waters before implementing them at a broader scale.
Retail: For the retail sector, 5G can provide trusted connectivity for enterprises to support peak-time traffic, keep a check on demand and supply through intelligent analytics, delivering real-time shopping experiences to consumers through AR/VR, and track the goods and services for efficient delivery mechanisms.
While 4G-driven applications enabled enterprises and their employees to stay connected over the internet during the pandemic, they could not create compelling use cases to help retailers manage the surge in demand for home delivery.
For example, since more and more people were homebound and following social distancing measures during the pandemic, the shipment volume proliferated. As a result, retailers had faced enormous stress to deliver the essentials on time using human resources.
Imagine, had there been a widespread 5G network available in India, retail enterprises would have been able to manage the surge in demand for home delivery during lockdowns, with a minimal human touch, by leveraging autonomous-delivery robots. The concept is not altogether new! It has already been tested and implemented in countries, such as the US, Sweden, and China.
For instance, in Stockholm, Sweden, European telecommunications operator, Tele2, leveraging 5G and IoT, recently collaborated with a food delivery partner to pilot Doora, a delivery droid to transport food delivery services across Stockholm during the pandemic.
Similarly, retailers across the globe are leveraging AR/VR tools to strengthen their sales and providing an exceptional customer experience. For instance, a couple of years back, German-based luxury car manufacturer, Audi, introduced a 360-degree Virtual Reality solution that lets consumers get a realistic view of their chosen car on their digital device. Customers can customize the car and change its color, accessories, using hundreds of possible configurations to shortlist the same.
“5G will enable cloud more efficiently, improve enterprise performance and pave the way for a new better-connected world. For instance, the low latency and exceptional bandwidth properties of 5G will significantly transform augmented and virtual reality use cases and raise the bar for immersive and engaging customer experiences. It will enable enterprises to conduct high-quality product and services virtual tours for their customers, especially those at remote locations where physical reach may be an issue,” says Pertisth Mankotia, CIO, Sheela Foam.
However, to achieve that consistently, firms in this sector need ultra-fast connectivity to improve productivity levels further and leverage the full potential of advanced technologies such as edge computing, cloud, AI, and machine learning.
With 5G, such immersive experiences will get much better, attract new customers, and improve enterprises’ revenues.
Healthcare and public safety: With the proper implementation strategies, 5G can be a big boon for enterprises operating in the healthcare and public safety domain. For example, 5G could enable city-based overloaded hospitals to deploy efficient remote patient monitoring capabilities and delivering quality healthcare through telemedicine.
The current inequality between people with quality broadband and those where it is still not available makes it difficult for healthcare professionals to create effective remote patient care mechanisms. To achieve with 5G, telecom service providers, such as Bharti Airtel, Vodafone-Idea, BSNL, and Jio will need to deploy the necessary infrastructure, signal repeaters, cells, and antennas.
According to PwC, remote care is just one area in which 5G can enable cost savings and better health outcomes. It says that 5G will improve efficiency and productivity in hospitals through advances such as 5G-enabled tracking of medical devices and patient beds and AI to 5G sensor data to trigger actions automatically and accelerate patient handovers.
By leveraging 5G network slicing, single network connections of 5G can be divided into multiple unique virtual links that help network providers prioritize specific users or devices regarding data connectivity.
“We have a couple of excellent customer stories around the use of IoT, and mainstream processing. One of the great stories out there is around our town here where we are based. We do flood plain management. We get much rain here, and because of the terrain and the surfaces here, it leads to flooding. And that is a safety issue, a public safety issue. And so we worked with the local town to install censors, take real-time data as the rain falls, detect and prepare for flood response and make sure that people understand that there is a large concern. All of that is fed through IoT-based sensors. The sensors are dependent on the cellular networks that are out there. So you can imagine the capability of 5G and the throughput, and I will say the breadth of data that we can consume through these connections. It is fascinating,” says Jay Upchurch, Executive Vice President & CIO, SAS India.
Revolutionizing manufacturing: The industrial sector is being touted as the biggest beneficiary of the fifth generation of wireless communications rollouts. Most manufacturing industries are now gearing toward smart factories and automating processes for better production and meeting dynamic demand-supply scenarios. Currently, manufacturers depend upon fixed-line networks to meet such requirements.
In the post-pandemic scenario, as businesses continue to acclimatize to the new ways of working, 5G holds immense potential to enable remote workers to improve performance by connecting and collaborating with their stakeholders in real-time.
Not only it equips the remote workforce with faster data processing capability to be more productive, but it also enables them to match the performance of standard office employees.
According to a Capgemini report, 5G in the Manufacturing Industry, in the near future, the industry will witness several other changes such as enhanced IoT that will accelerate the communication between all the connected devices across the spectrum of a factory, from the shop floor to the warehouse and assembly line, enabling real-time control for manufacturers to adjust the process in motion. In addition, 5G will help businesses exploit the massive amount of data collected from operations faster to be utilized for predictive maintenance and monitoring and augmented reality.
“Latency has been a significant deterrent in the way of building a truly autonomous enterprise. There are many autonomous use cases across industries that are ready from a technology standpoint but need ultrafast connectivity to succeed,” says Rajesh Aggarwal, Head of IT, Aamor Inox, a leading manufacturer, and exporter of Stainless Steel Bright Bars in India.
Rajesh further elucidates that the ultra-low latency provided by 5G can help overcome the obstacles faced by enterprises in deploying mission-critical applications. “In the manufacturing sector, 5G will empower enterprises to implement Industry 4.0 technologies effectively. Additionally, it will enable them [businesses] to gather timely valuable data insights so that they can monitor equipment in real-time for increased production, compliance, and safety,” he adds.
Large organizations, such as Airbus, Ford, Whirlpool, and Worcester Bosch are some early adopters or testers of enterprise 5G networks. Worcester Bosch is one of the first organizations to launch 5G enabled smart factory. The factors comprise advanced sensors for preventive maintenance and generate real-time analysis using AI-based analytics to anticipate any potential failures.
According to a KPMG report, titled Unlocking the benefits of 5G for enterprise customers, in the manufacturing sector, the pervasive 4G thinking typically creates a linear process where materials are ordered, machines are preset and managed by people maintained by lifetime without any wear and tear. But, unfortunately, this creates a high potential for costly breakdowns and waste and a process that cannot quickly respond to changes in demand. And deploying 5G into this kind of environment can support a business transformation enabling dynamic, self-regulating, and self-adjusting processes that translate into agility, speed, and higher productivity.
Eventually, these benefits get passed onto the end customer in the form of customization, quality, and speed of delivery. “The linear process becomes circular and significant value is created,” the KPMG report adds.
In addition to the above, 5G is also expected to create tremendous new opportunities for sectors, such as agriculture, media and entertainment, and financial services. Automation of agricultural systems will enable enterprises operating in this domain to collect real-time data, counsel farmers to increase productivity. In financial services, the technology will allow enterprises to execute complex processes such as Video KYC for obtaining credit at ease. In addition, 5G will enable them to provide unique customer experiences such as video and introducing new innovative mobile apps that support AR and VR experiences.
Driving innovations
5G will cause a massive boom in the use of sensors around us, generating a humongous amount of data to make connected farms, smart cities, and intelligent buildings a reality. Through its ubiquitous coverage, the 5G technology enhances enterprises’ time-sensitive automation capabilities by powering millions of IoT-connected devices, helping them work with their stakeholders and users proactively.
Another area where 5G can be instrumental in pushing more and more compute and capability to the edge. In IoT-enabled devices, if networks cannot handle data transmission, it’s a lost cause for business. So, it is critical to get the data as soon as possible from the source device so that AI systems can do the analysis and send it to designated people or machines to take action.
Over the next, eight to ten years, widely accessible 5G networks are likely to shape the experiences of businesses and consumers and provide significant digital momentum to all industries. According to PwC, 5G-driven applications in healthcare, smart utilities, consumer and media, industrial manufacturing, and financial services together are expected to add a massive USD 1.3 tn to global GDP by 2030.
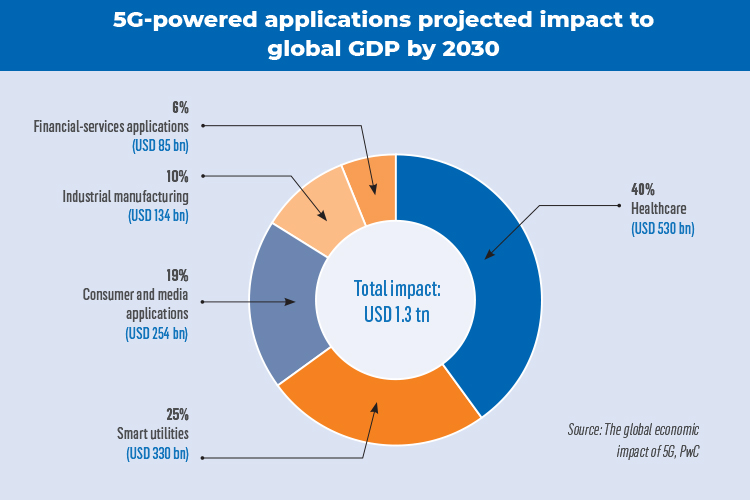
Key challenges
Despite all the benefits and several countries rolling out 5G technology, India still lags in infrastructure readiness for the next technological breakthrough. While the government has indicated that the spectrum auctions will happen soon, the country faces a plethora of concerns: lack of use cases/business models, availability of network equipment, and immature device ecosystem.
“There is no doubt that 5G technology stands out as a real game-changer, but I am not sure if we have been able to leverage 4G fully yet. Even today, we are not getting the bandwidth that is needed to run the business. The technology [5G] looks great for all theoretical purposes, but on a practical note, we [India] are not ready from an infrastructure standpoint. There is no technology or application readiness in our country,” says Ajitsingh Nawale, Head of IT at Mahindra CIE Automotive.
Among enterprises, there are also concerns that to sustain 5G and align it with legacy infrastructure, massive investments might be needed, yet considering the country’s present state of infrastructure, they might not get the desired outcomes or productivity gains.
Also, since there are no sufficient 5G use cases in India yet, there could be several complexities at the backend algorithms that might need CIO attention. For example, while an algorithm takes x number of seconds in the current ecosystem, in a 5G environment, it might take x number of nanoseconds. This is a complex scenario for some CIOs who feel that they are unsure if they can run those applications for consumers on the fly and what kind of business benefits it will deliver to the end-user?
Agrees Milind Khamkar, Group CIO at Super-Max, “With more and more people are using remote connectivity to reach each other; the high-speed fifth-generation network is a blessing for everyone. However, its success will be dependent upon how the overall infrastructure gets developed. Because even though we are using 4G today, many gaps [such as poor infrastructure] are still prohibiting us from leveraging the full potential of this technology. Enterprises, telcos, and government need to collaborate to make 5G successful in India,” he elucidates.
Rajesh Aggarwal advises that enterprises should avoid implementing 5G technology at pan India but instead focus on pilot rollouts where there is a high density in 5G. “To gauge the productivity levels 5G can bring for you; enterprises need to test it out in terms of application and transaction. There could be several complexities in the backend using legacy systems.”
High-speed connectivity also comes with new security-related threats. With 5G networks expected to be the mainstay for critical IT applications, such as IoT and AI in the future, telecom service providers are expected to improve the ancillary services for robust and secure enterprise connectivity.
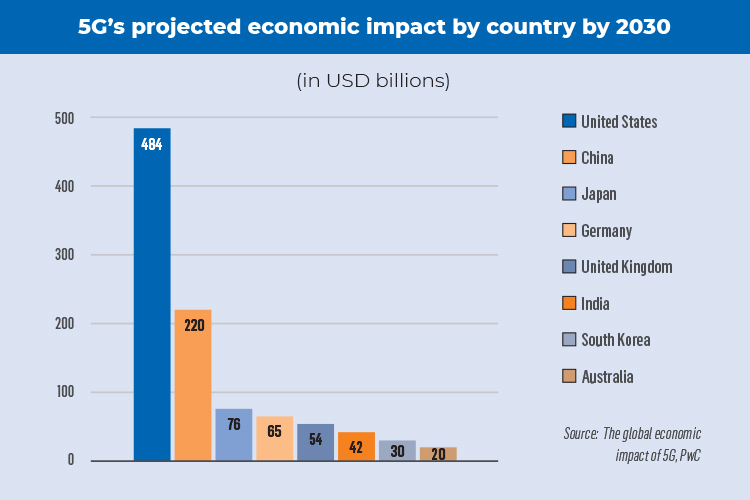
What’s ahead?
In the years ahead, 5G transformation will help businesses reinvent themselves, improve their productivity levels and help unlock new revenue streams.
“5G can simplify the complexities of diverse working ecosystems. Because of the COVID crisis that we are going through, there are various modalities of working today. For a distributed workforce environment to succeed, one needs the availability of robust high-speed bandwidth [like of 5G] across all locations so that employees can seamlessly connect to multiple organizational ecosystems securely and work becomes business-as-usual,” says Nirvan Biswas, CTO, National Bulk Handling Corporation & Infinity Fincorp (NBHC).
The telecom industry association, GSMA, anticipates that by 2025, 5G networks are likely to cover one-third of the world’s population. “Each industry has its own specific set of 5G-based IoT use cases in mind, while their attitudes to 5G suppliers and supporting ecosystems also vary substantially. Despite these differences, the crisis brought about by the COVID-19 global pandemic is placing a new emphasis on industry resilience and innovation, now and in the future. 5G can play a vital role in achieving this, but only if 5G providers become more vertical-specific in their interactions with enterprises,” notes EY report.
In India, 5G’s contribution to economic growth may be very minimal for the next few years. Still, this timeframe will be critical for governments and telecom companies to build essential infrastructure and allocate the necessary spectrum for developing robust and industry-wide 5G use cases.

 In
In
Add new comment