
Blockchain is a technology for a new generation of transactional applications that establishes trust, accountability and transparency while streamlining business processes. It is a design pattern made famous by bitcoin, but its uses go far beyond. With it, we can re-imagine the world's most fundamental business interactions and open the door to invent new styles of digital interactions. It has the potential to vastly reduce the cost and complexity of cross-enterprise business processes. The distributed ledger makes it easier to create cost-efficient business networks where virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded—without requiring a central point of control.
The application of this emerging technology is showing great promise across a broad range of business applications.
For example, blockchain allows securities to be settled in minutes instead of days. It can also be used to help companies manage the flow of goods and related payments, or enable manufacturers to share production logs with OEMs and regulators to reduce product recalls.
The Problem and the Solution
Before
Asset ownership and transfer between businesses is currently inefficient, slow, costly and vulnerable to manipulation. Everyone has their own ledger where discrepancies between business parties can increase settlement times.
A new way is needed for Internet-age market enablement.
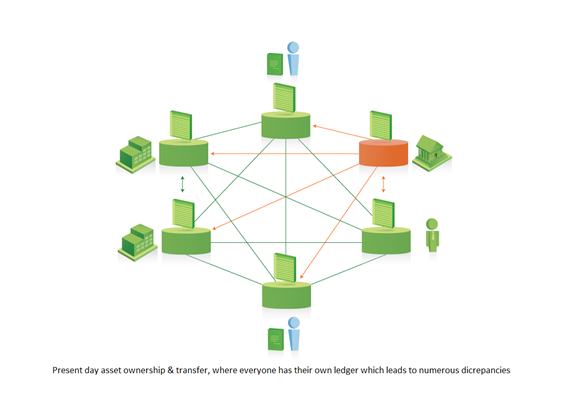
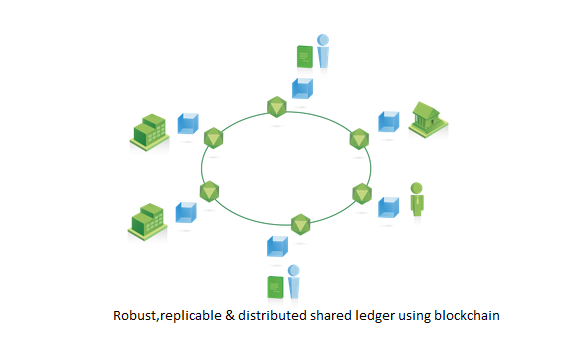
After
Blockchain technologies can be used to share a ledger across the business network. The network will be private to the parties concerned, permissioned so only authorized parties are allowed to join, and secure using cryptographic technology to ensure that participants only see what they are allowed to see.
The shared ledger will be more robust, since it is replicated and distributed. All transactions against the ledger will require consensus across the network, where provenance of information is clear and transparent. Transactions will be immutable (unchangeable) and final.
The business network participants will be the same - disintermediation is not a natural consequence of blockchain usage.
Goods and services are provided more efficiently, with the potential to lower costs at all levels.
Key concepts of blockchain
A blockchain has two main concepts. A business network, in which members exchange items of value through a ledger, which each member possesses and whose content is always in sync with the others.
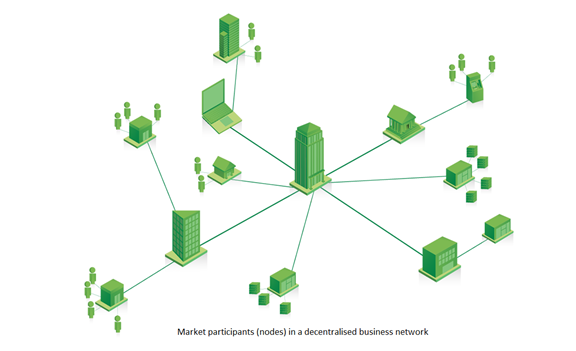
A business network
● A decentralized peer-to-peer architecture with nodes consisting of market participants (such as banks and securities firms).
● Protocol peers validate and commit transactions in order to reach consensus.
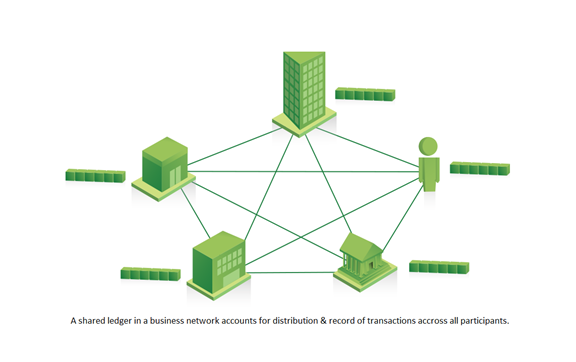
Shared ledger
It can act as a source of truth for businesses doing transactions on a blockchain:
● Records all transactions across the business network
● Is shared among participants
● Is replicated so each participant has their own copy
● Is permissioned, so participants see only appropriate transactions
Often, companies have multiple ledgers for multiple business networks in which they participate. It can be used for recording and totaling financial transactions.
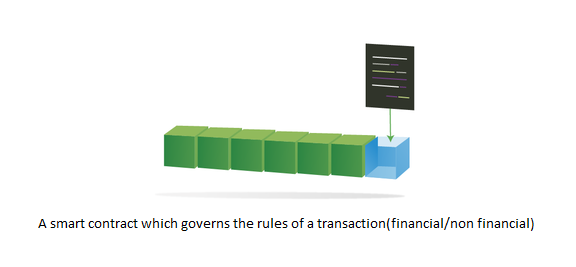
Smart contracts
A smart contract can include a digital asset which is anything that has an owner and can be converted into value. Digital assets can be tangible or intangible. A smart contract can also include a digital representation of a set of business rules:
● Is embedded in the blockchain
● Is executed in a transaction
● Is verifiable, signed, and encoded in a programming language
For example, it defines conditions under which corporate bond transfer occurs.
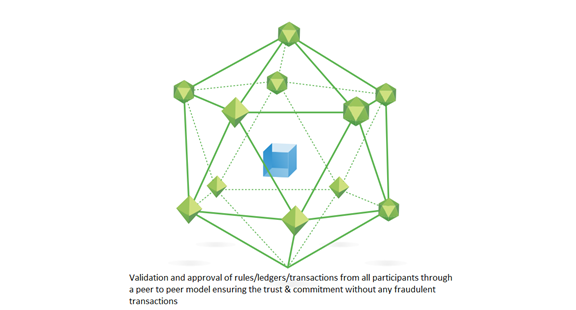
Consensus
Entries in the ledger are synchronized to all ledgers in the network. Consensus ensures that these shared ledgers are exact copies, and lowers the risk of fraudulent transactions since tampering would have to occur across many places at exactly the same time.
● All parties agree to the transaction and validate it via the peer network.
● Rules can also be established to validate transactions.
● This trusted and trustless participation makes commitment possible at a low cost.
IBM Blockchain uses a “pluggable” consensus system to meet the needs of different industry segments.
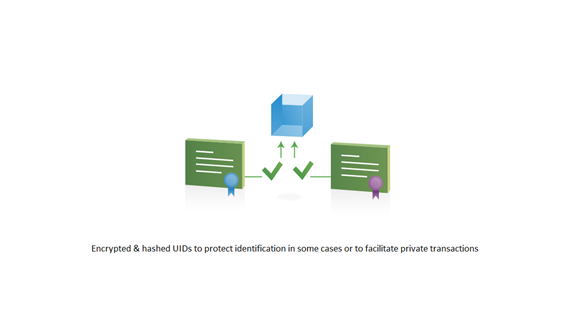
Privacy and confidentiality
Ability to protect records with a personal digital signature — the blockchain generates a private and public key to seal that record.
● It is encrypted, hashed, and sent to the network of validating nodes
● Unique IDs for customer, invoice and reference numbers
Although the ledger is shared, sometimes participants require:
● Private transactions
● Identities those things which cannot be linked to specific transactions
Transactions need to be authenticated, and cryptography is central to these processes.
The potential of blockchain, based on my understanding of studying the fintech economy and working with global projects in fintech domains for clients across continents, is immense.
The author is the co-founder of Sodio Technologies, a mobile application development company.

 In
In
Comments
Healthy Man Complaints https
Healthy Man Complaints https://bbuycialisss.com/ - where to buy cialis online forum Medicament Amoxil <a href=https://bbuycialisss.com/#>Cialis</a> Generique Baclofen 25mg
Healthy Man Complaints https
Healthy Man Complaints https://bbuycialisss.com/ - where to buy cialis online forum Medicament Amoxil <a href=https://bbuycialisss.com/#>Cialis</a> Generique Baclofen 25mg
Add new comment